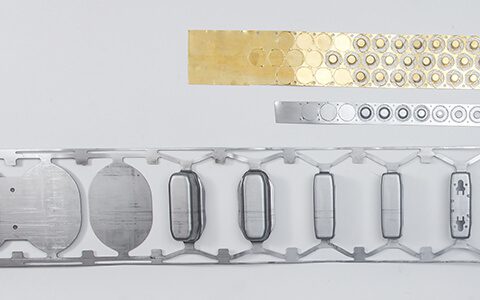
Stamping
Stamping is a manufacturing technique that uses a flat, thin sheet of metal to produce an object whose shape is not developable.
The principle of stamping is the plastic deformation of the metal, consisting of the local elongation and contraction of the sheet to obtain the shape.
Studying the final part required by the customer enables our engineers to back-calculate the steps involved in shaping the material to define a flat blank and work out the best strip design.
A technical and costing study (part geometry and complexity, dimensional tolerances, materials, etc.) is carried out so that we can put forward one or more technical solutions, determine a process, then a production operation sheet, and finally present prototypes and initial samples before approval for series production.
Materials
All metals
- cuprous metals: copper, brass, bronze, nickel silver, beryllium copper, etc.
- steels: high and low carbon, high-yield, silicon steel (electrical plate), etc.
- all grades of stainless steel: AISI 301, 304 (L), 316 (L), 430, etc.
- all grades of aluminium
- special and custom alloys: tantalum, titanium, special copper alloys (Cuprofor), etc.
- other (metallic and non-metallic) materials on request, after validation of a representative sample


Parts
- 1Dimensions handled :
- Thickness: from 0.03 mm to 8.00 mm (depending on the material and geometry of the part)
- Feed strip width: from 3.00 mm to 500 mm (depending on the material and geometry of the part)
- 2Part forming and assembly process :
- Blanking, cambering
- Stamping
- Drilling, flow drilling, tapping, chamfering, specific machining operations
- Welding, crimping, clinching, etc.
- 3Subcontracted treatments :
- Degreasing, tribofinishing
- Heat treatment
- Surface treatment (tin plating, zinc coating, silvering, gilding, rhodium plating, etc.) painting, shot peening, etc.
- Precision fine sheet metal work, bar turning, etc.
- 4Batch size :
- No minimum production run: we can procure the materials and mount tools to make a single part if necessary
- Fixed and variable costs are calculated according to the size of the batch required by the customer
- Maximum batch size depends on the technical characteristics of the part: geometry, dimensions, thickness, material, etc.
- 5Capacities :
- Maximum production capacity of up to 1,500 strokes per minute over several shifts
- Maximum batch size of several million parts.
Production – Maintenance
We have all the right equipment to produce and maintain our tools, including EDM machines, surface grinders, lathes and milling machines